
The cost accounting system so installed, accomplishes one of the twin objectives of cost accounting, viz., cost ascertainment. Economizing could towards a more conservative view taking an analytical approach and concentrating on the smooth and consistent way of spending.
Effective cost reduction strategies are essential for sustaining profitability and gaining long-term financial resilience. Beyond just lowering expenses, these strategies help businesses reallocate resources, improve performance, and create a solid foundation for scalable growth and market adaptability. For example, software like SAP or Oracle Cost Management helps organizations analyze spending patterns, identify inefficiencies, and implement corrective measures. This centralized approach to cost control ensures transparency and accountability, making it easier to meet financial targets without overspending. Implementing cost monitoring systems helps businesses track expenses in real-time and identify potential inefficiencies.
What roles and tasks does https://bushwire.org/cpa-licensure-accounting-bsba-university-of-san/ everybody have in an overall cost reduction program? How does the strategy change over time in the face of market fluctuations, changes in consumer demand, and the introduction of new technologies and competition? And how do the relationships between your business departments impact cost analysis? For instance, one might attribute high spending in the accounting department to an inefficient procurement policy. A lot can go wrong in cost reduction, and messy implementation can ruin an otherwise excellent effort. Accidentally cutting critical expenses can reduce the quality of your products, make the job harder for your employees, jeopardize your operations, and actually lower your profits in the end.

For instance, travel expenses can be automatically allocated to a project code, providing clarity on project costs. Automated allocation reduces errors, enhances transparency, and supports strategic cost control efforts. For example, the system highlights suppliers with higher costs or inconsistent delivery, allowing Foreign Currency Translation organizations to make informed decisions about contract renewals.

Objectives should align with the broader business strategy and take into account both short-term gains and long-term sustainability. Clear targets also help motivate teams and provide a reference point for evaluating success throughout the process. Effective oversight requires leadership engagement, accurate reporting systems, and timely reviews—all of which create a culture of disciplined financial stewardship across the business.
For example, a company might adopt green energy solutions to mitigate rising energy prices or comply with regulatory changes to avoid potential fines or penalties. Cost avoidance focuses on future-proofing the organization against potential financial risks. For example, the success of investing in employee training might be evaluated by observing a decline in workplace accidents and related costs control and reduction definition compared to previous years.
Each satellite represents a vital aspect of this broader field, and each is presented as a domain. Glossaries illuminate the key concepts, terminology, and challenges within each area, allowing to build a more complete and nuanced understanding of the interconnected world. Productivity may be defined as the ratio between the production of a given commodity measured by volume and one and more of the corresponding input factors also measured by volume. Uniform Costing is the use by several undertakings of the same costing principles and/or practices. Job evaluation define as “a practice which seeks to provide a degree of objectivity in measuring the comparative value of jobs within an organization and among similar organizations”.
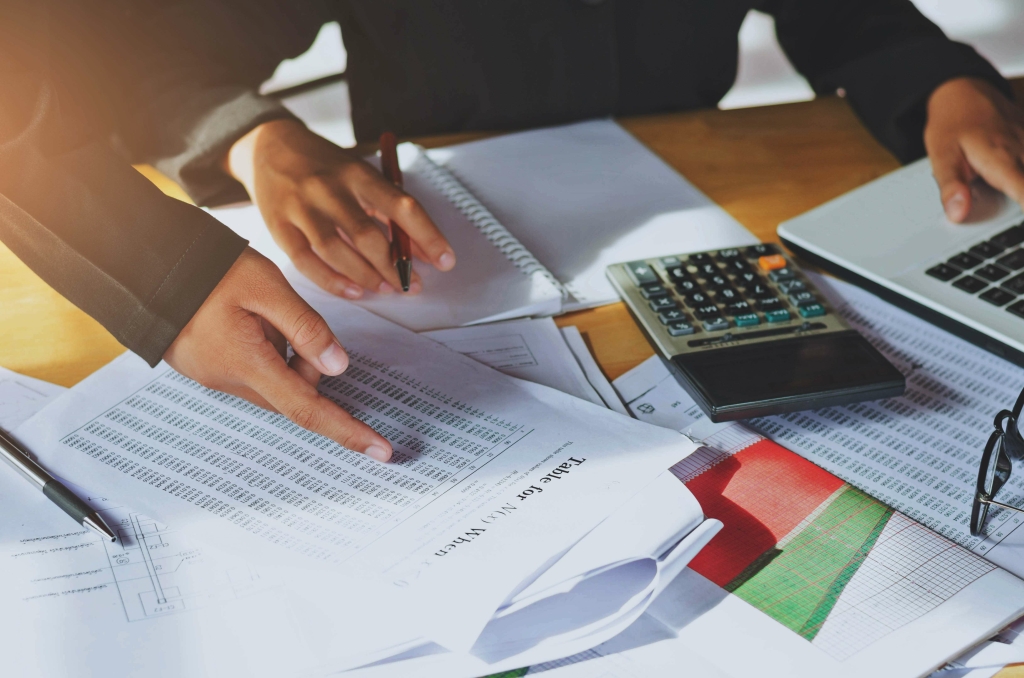

In organizations the budget is a financial plan that outlines projected revenues and expenses over a specific period. It serves as a benchmark for cost control efforts by setting limits and targets for various cost categories. Monitoring actual expenses against the budget allows organizations to identify deviations and take corrective actions. It aims to strike a balance between minimizing costs without compromising the quality of products or services.
In other words, the objective of cost control is the performance of the same job at a lower cost or a better performance for the same cost. (v) No amount of detailed analysis of the cost of variances can undo what has already been done; however, control measures should ensure that such mistakes are not repeated. The only way to prevent excess costs in practice is for the manager to take action before the event. The component of the cost reduction strategy targets a budget permanently lowering the overall cost functions of the organisation. Insurance companies are highly motivated to encourage and incentivize risk reduction practices, as managing claims can be costly. In addition to covering property or liability claims, the process of investigating and handling claims can also be expensive.
Better cash flow translates to greater liquidity, reduced reliance on credit, and more financial agility. Lower operating costs create the financial flexibility needed to pursue growth without overleveraging or risking cash reserves. Outsourcing non-core activities—such as IT support, payroll, or customer service—can significantly reduce labor and overhead costs.